A water soluble antibiotic Highly effective against respiratory problems May be used during competition and racing season Composition Contains spiramycin adipate 1 500 000iu/g Water soluble powder Dosage and Administration Administer 1 teaspoon per gallon of drinking water Dosage may be doubled in the case of severe infectionPLQDGTZICFBBSODPUAUXBSSAN Spiramycin adipate Similar structures search, synonyms, formulas, resource links, and other chemical information Spiramycin is a 16membered ring macrolide discovered in 1952 as a product of Streptomyces ambofaciens that has been available in oral formulations since 1955, and parenteral formulations since 1987 Resistant organisms include Enterobacteria, pseudomonads, and moulds Type Small Molecule Groups Approved Structure
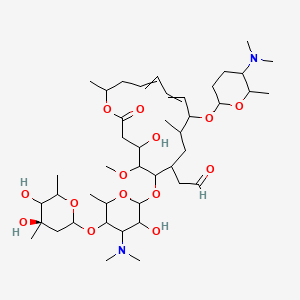
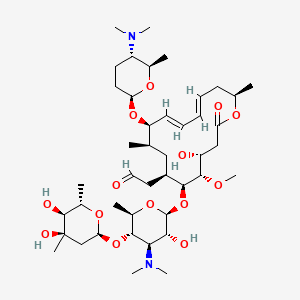
Rovamycin C43h74n2o14 Pubchem
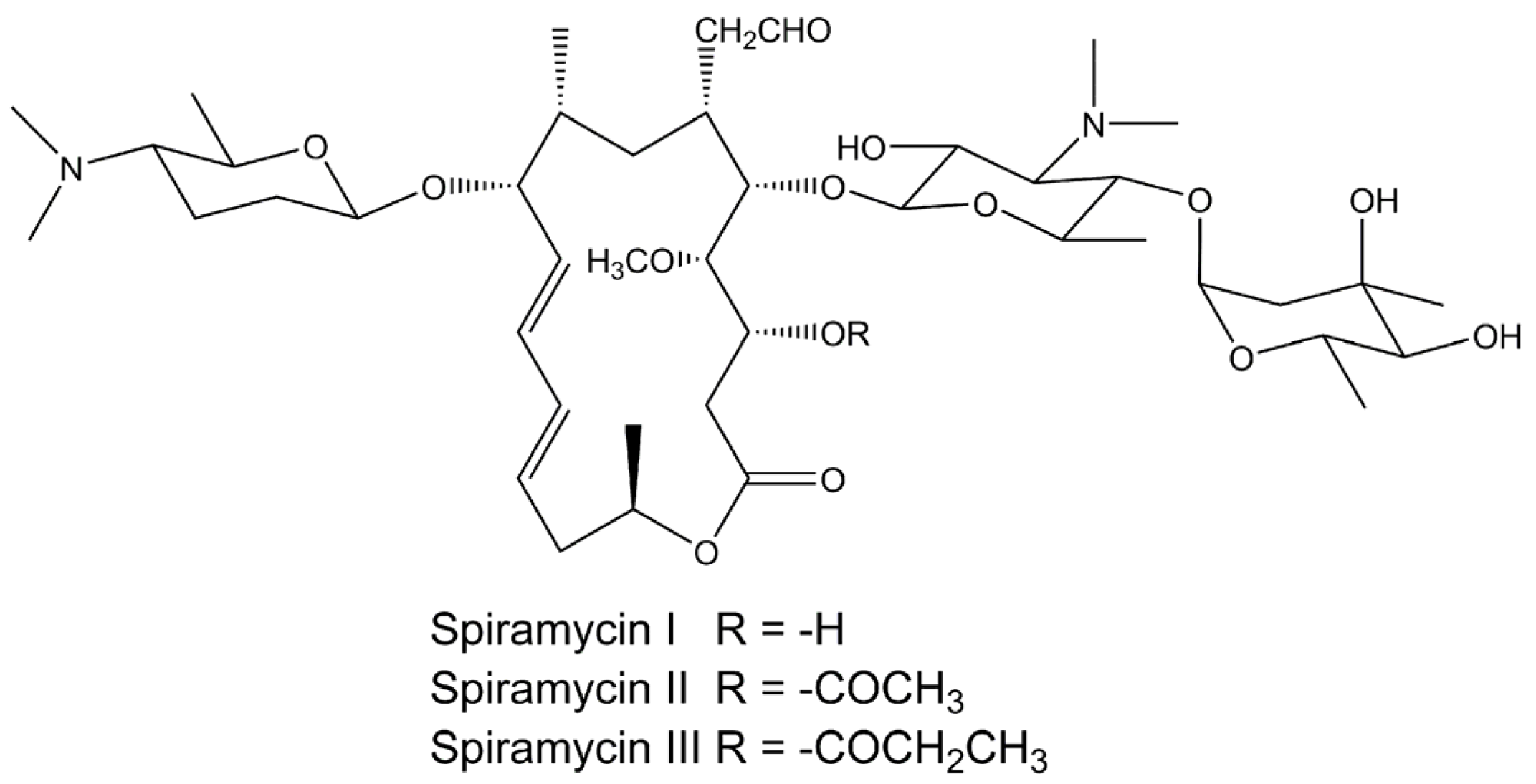
Spiramycin structure
Spiramycin structure-Spiramycin, a 16membered lactone ring macrolide, has been in clinical use for the past 15 years with little serious associated toxicity GI disturbance has usually been mild & no changes in GI motility have been noted either experimentally or in humans, in contrast to other macrolides, such as erythromycin Allergic reactions have been uncommon & mainly restricted to transient skinNew formulations of spiramycin suitable for oral administration, particularly for children, comprise spiramycin and potassium acesulfame These formulations mask the bitterness of spiramycin without adversely affecting the bioavailability or stability of the spiramycin Preparation by wet granulation followed by dry state mixing is also disclosed




A Chemical Structure Of Spiramycin Pk 7 9 B Dose Dependent Download Scientific Diagram
Spiramycin adipate C49H84N2O18 CID structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biologicalSpiramycin is a 16membered ring macrolide It was isolated in 1954 as a product of Streptomyces ambofaciens by PINNERTSINDICO As a preparation for oral administration it has been used since 1955, in 1987 also the parenteral form was introduced into practice An antibiotic used for the treatment and control of a number of bacterial and mycoplasmal infections in animals and also used as a growth promotor Availability status Introduction & key dates 00, Europe Examples of species treated Poultry, Sheep, Cattle, Pigs, Cats, Dogs Chemical structure Isomerism
Spiramycin approved in the EU, and in other countries; Spiramycin is used to treat many kinds of infections It is often used to treat toxoplasmosis in pregnant women since this medicine decreases the chance that the unborn baby will get the infection This medicine may also be used for other problems as determined by your doctor It will not work for colds, flu, or other virus infectionsAbstract Spiramycin was less active than erythromycin in vitro against sensitive strains of Staphylococcus aureus, but was as effective against staphylococcal infections in mice when the drugs were administered immediately after infection spiramycin was relatively more effective in prophylactic experiments when the antibiotics were administered at 4 or at 6 hr before infection
Huisgen cycloaddition allowed obtaining novel triazolebridged antibiotics (616) with the reconstructed C(5) arm of spiramycin 1H1H NOESY couplings indicated the structureAdult 46 tab daily in 23 divided doses (Spiramycin 345 MIU and Metronidazole mg) Children 10 to 15 yrs 3 tab daily (Spiramycin 225 MIU and Metronidazole 375 mg) Children 6 to 10 yrs 2 tab daily (Spiramycin 15 MIU and Metronidazole 250 mg) Schedule of Metronidazole Spiramycin N/A Storage Requirements for Metronidazole SpiramycinStructure activity relationships of spiramycins Omura S, Sano H, Sunazuka T Sixtysix derivatives of spiramycin I and neospiramycin I were synthesized and evaluated by four parameters, MIC, affinity to ribosomes (ID50), therapeutic effect in mice and retention time in HPLC




Rovamycin C43h74n2o14 Pubchem




Significant Reduction Of Brain Cysts Caused By Toxoplasma Gondii After Treatment With Spiramycin Coadministered With Metronidazole In A Mouse Model Of Chronic Toxoplasmosis Antimicrobial Agents And Chemotherapy
Find Spiramycine and related products for scientific research at MilliporeSigma Structure Search Relevance Compare Keyword 'Spiramycine' Spiramycin Spiramycin Synonyms Formacidine, Spiramycin CAS Number EC Number Product Number Product Description SDS;CHEBI spiramycin II A macrolide antibiotic produced by various Streptomyces species This entity has been manually annotated by the ChEBI Team No supplier information found for this compound A molecular entity capable of accepting a hydron from a donor (Br o nsted acid) A drug used to treat or prevent bacterial infectionsSpiramycin manufacturer in India Exporter in India Spiramycin 15 million iu,Spiramycin 3 million iu Largest Generic Manufacturer,drugs,Formula,producing Spiramycin MSDS,COA,pdf,doc chemical api method according to the present Spiramycin invention Suppliers List,Molecular Structure,Weight,IUPAC,Synonyms for Spiramycin



Actascientific Com Asds Pdf Asds 02 0249 Pdf



123bio Net Cours Les Differentes Classes D Antibiotiques
(The Expresswire) Global "Acetylspiramycin (CAS ) Market" (2126) Research Report presents an indepth evaluation of the marketAverage mass Da;8 rows Crystal structures of the Haloarcula marismortui large ribosomal subunit complexed with the 16membered macrolide antibiotics carbomycin A, spiramycin, and tylosin and a 15membered macrolide, azithromycin, show that they bind in the polypeptide exit tunnel adjacent to the peptidyl transferase center
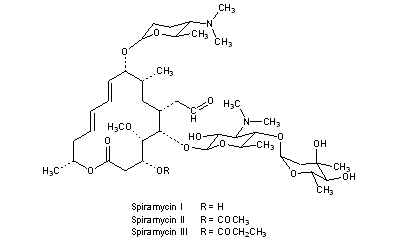



Spiramycin



Analyticalsciencejournals Onlinelibrary Wiley Com Doi Pdf 10 1002 Sscp
Monoisotopic mass Da;Spiramycine has affinity with lung tissue and the mucus membranes of the nasal passage and pharynx and is highly active against most grampositive bacteria, mycoplasma, chlamydia and in this way is an ideal drug for the treatment of bronchial infections INDICATIONS Respiratoy Infections Ornithosis The usual dose is 25 mg (75,000 IU) per kg (114 mg per pound) of body weight two times a day, or 17 mg (51,000 IU) per kg (77 mg per pound) of body weight three times a day Adults and teenagers—500 mg (1,500,000 IU) injected slowly into a vein every eight hours For severe infections, the dose is 1 gram (3,000,000 IU) injected slowly into



A Comprehensive Review Of Toxoplasma Gondii Biology And Host Cell Interaction Challenges For A Plant Based Vaccine Springerlink




Diploma Project Qualifier Le Generique Typographic Interface For Generic Drugs Laurette Colmard
Ketolides Ketolides are a class of antibiotics that are structurally related to the macrolides They are used to treat respiratory tract infections caused by macrolideresistant bacteriaNational Institutes of Health Crystal structures of the Haloarcula marismortui large ribosomal subunit complexed with the 16membered macrolide antibiotics carbomycin A, spiramycin, and tylosin and a 15membered macrolide, azithromycin, show that they bind in the polypeptide exit tunnel adjacent to the peptidyl transferase center Their location suggests that they inhibit protein synthesis by



Analyticalsciencejournals Onlinelibrary Wiley Com Doi Pdf 10 1002 Sscp
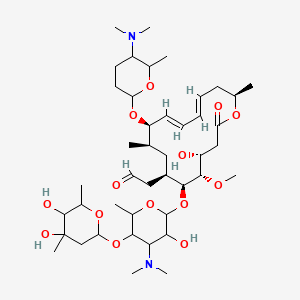



2 4r 5s 6s 7r 9r 10r 11e 13e 16r 6 5 4 5 Dihydroxy 4 6 Dimethyloxan 2 Yl Oxy 4 Dimethylamino 3 Hydroxy 6 Methyloxan 2 Yl Oxy 10 5 Dimethylamino 6 Methyloxan 2 Yl Oxy 4 Hydroxy 5 Methoxy 9 16 Dimethyl 2 Oxo 1 Oxacyclohexadeca 11 13 Dien 7 Yl
View All Manufacturers & Suppliers of Spiramycin API with Drug Master Files (DMF), CEP/COS, Japanese DMFs, Written Confirmation (WC) details listed on PharmaCompasscomTylosin/tylocine used in animals; Spiramycin (SPY) is a macrolide antibacterial that is used similarly to erythromycin in the treatment of susceptible bacterial infections It has also been used, alone or in combination with MNZ, in the protozoal infections, cryptosporidiosis and toxoplasmosis ( 1 )



Spiramycin I C43h74n2o14 Chemspider




Pdf Effect Of Spiramycin And Tulathromycin On Abomasal Emptying Rate In Milk Fed Calves Peter Constable And Mohammad Hajikolaei Academia Edu
Spiramycin Regulatory process names 2 IUPAC names 3 Other identifiers 1 Molecular structure The molecular structure is based on structures generated from information available in ECHA's databases If generated, an InChI string will also be generated and made available for searching This information is only displayed if the substanceWere identified and their structure confirmed by mass spectrometry Residues of parent drug accounted for 04 mg/kg, while residues of spiramycin adducts with Lcysteine represented 105 mg/kg, and neospiramycin adducts with Lcysteine accounted for– Spiramycin does not penetrate into the CSF – It passes into breast milk and binds with plasma proteins (approximately 10%) Metabolism Spiramycin is slowly inactivated in the liver, with formation of unknown metabolites Excretion – Biliary elimination is very extensive;




Glycosylation Steps During Spiramycin Biosynthesis In Streptomyces Ambofaciens Involvement Of Three Glycosyltransferases And Their Interplay With Two Auxiliary Proteins Antimicrobial Agents And Chemotherapy




Kegg Drug Spiramycin Embonate
Consumer information about the medication SPIRAMYCIN ORAL CAPSULE , includes side effects, drug interactions, recommended dosages, and storage information Read more about the prescription drug SPIRAMYCIN ORAL CAPSULESpiramycin is a 16membered ring macrolide antibiotic from Streptomyces ambofaciens It inhibits bacterial protein synthesis at the level of peptidytRNA dissociation from ribosomes It is mainly used against Grampositive bacteriaTo the Spiramycin residue monograph prepared by the 43rd meeting of the Committee and published in FAO Food and Nutrition Paper 41/7, Rome 1995 Introduction As the sponsor was unable to provide a validated chemical method for the analysis of spiramycin and neospiramycin residues in pig tissues to the 43rd JECFA meeting in 1994, it was not



Http Www Fao Org Fileadmin User Upload Vetdrug Docs 41 4 Spiramycin Pdf




Spiramycin Cas 8025 81 8 Scbt Santa Cruz Biotechnology
Troleandomycin used in Italy and Turkey;Spiramycin is a complex formed by three major components (I–III), which differ in the substituent at position 3 of the lactone nucleus The spiramycins are more stable than erythromycin A in an acidic medium Roxithromycin is highly stable at pH 42 (Figure 1414)Spiramycin (Formacidine) is a 16membered ring macrolide (antibiotic) Spiramycin reduces the hygromycin A protections of nucleotides in 23 S rRNA 1 Spiramycin, a 16membered macrolide, inhibits translocation by binding to bacterial 50S ribosomal subunits with an apparent 11 stoichiometry Spiramycin acts primarily by stimulating the



2




Figure 2 From Genome Mining Of Streptomyces Ambofaciens Semantic Scholar
Spiramycin I Molecular Formula C 43 H 74 N 2 O 14; Spiramycin is a macrolide antibiotic and antiparasitic It is used to treat toxoplasmosis and various other infections of soft tissues Although used in Europe, Canada and Mexico, spiramycin is still considered an experimental drug in the United States, but can sometimes be obtained by special permission from the FDA for toxoplasmosis in the firstSpiramycin I ChEBI ID CHEBI Definition A macrolide antibiotic produced by various Streptomyces species that is used to treat toxoplasmosis and various other infections of soft tissues Stars This entity has been manually annotated by the ChEBI Team Secondary ChEBI IDs




Why Chloramphenicol Is Banned Ballya



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html
As a member of the wwPDB, the RCSB PDB curates and annotates PDB data according to agreed upon standards The RCSB PDB also provides a variety of tools and resources Users can perform simple and advanced searches based on annotations relating to sequence, structure and function These molecules are visualized, downloaded, and analyzed by users whoLevels are 15 to 40 times higher than those in serumStructureactivity relationships and molecular modelling indicated that 8r, 14r and q may have different binding sites compared to current erythromycins Moreover, 8r, 14r and q have 25–36




Spiramycin Semantic Scholar



Spiramycin C43h74n2o14 Pubchem
Spiramycin is used to treat many kinds of infections It is often used to treat toxoplasmosis in pregnant women since spiramycin decreases the chance that the unborn baby will get the infection Spiramycin may also be used for other problems as determined by your doctor It will not work for colds, flu, or other virus infectionsSpiramycin is a 16membered ring macrolide (antibiotic) Stability and Solubility Advice Information concerning product stability, particularly in solution, has rarely been reported and in most cases we can only offer a general guideSearches without any special characters (listed below) will return items that contain the exact value(s) entered in the search field



160



Spiramycin 8025 81 8
Spiramycin is a medicine available in a number of countries worldwide A list of US medications equivalent to Spiramycin is available on the Drugscom websiteSpiramycin is used to treat the condition of toxoplasmosis in women who are pregnantIt is an anti bacterial that helps to prevent the spread of the infection to the unborn baby It must be noted however that it will not affect the seriousness of the condition in the already affected babySpiracle, in arthropods, the small external opening of a trachea (respiratory tube) or a book lung (breathing organ with thin folds of membrane resembling book leaves) Spiracles are usually found on certain thoracic and abdominal segments In elasmobranch and ganoid fishes a pair of spiracles,




Macrolide Antibiotics Spiramycin Carbomycin Angolamycin Methymycin And Lancamycin Springerlink




Lifelong Persistence Of Toxoplasma Cysts A Questionable Dogma Trends In Parasitology
Spiramycin is a macrolide antibiotic, and it belongs to the same class with the antibiotics Erthromycin, Azithromycin, and Telithromycin Spiramycin is a prescription drug Like many other antibiotics, Spiramycin does not work and will not treat737 Spiramycin (WHO Food Additives Series 29) SPIRAMYCIN First Draft prepared by Dr KN Woodward Veterinary Medicines Directorate Weybridge, Surrey, England 1 EXPLANATION Spiramycin is a macrolide antibiotic used for the treatment and control of a number of bacterial and mycoplasmal infections in animals




Spiramycin 8025 81 8




A Chemical Structure Of Spiramycin Pk 7 9 B Dose Dependent Download Scientific Diagram



Coa Of Spiramycin Certificate Of Analysis Abmole Bioscience




Structures Of Spiramycins Neospiramycins Spiramycins U And S And Download Scientific Diagram




Antibiotics Pdf Penicillin Drugs




Significant Reduction Of Brain Cysts Caused By Toxoplasma Gondii After Treatment With Spiramycin Coadministered With Metronidazole In A Mouse Model Of Chronic Toxoplasmosis Antimicrobial Agents And Chemotherapy




Spiramycin 8025 81 8



Academic Oup Com Jac Article Pdf 22 Supplement B 93 22 Supplement B 93 Pdf




Chemical Structures Of Main Components Of Spiramycin And Its Related Download Scientific Diagram



Journals Sagepub Com Doi Pdf 10 1177




Antibacterial Inactivation Of Spiramycin After Titanium Dioxide Photocatalytic Treatment Sciencedirect



Spiramycin スピラマイシン Drug Approvals International
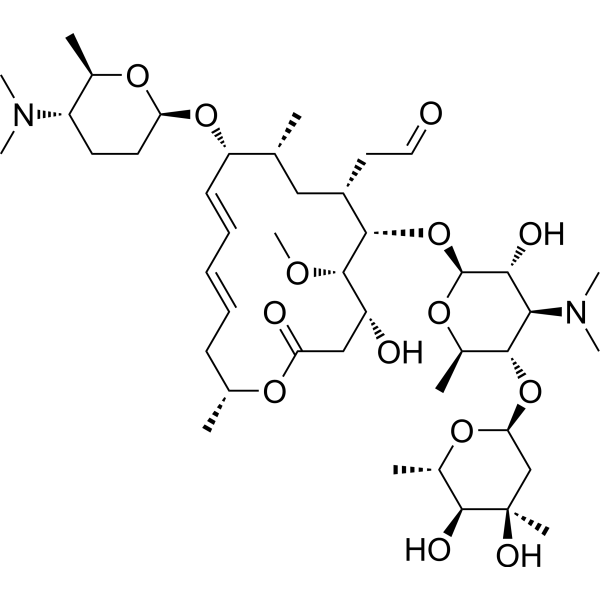



Spiramycin Rovamycin Antibiotic Medchemexpress




Spiramycin Structure C43h74n2o14 Over 100 Million Chemical Compounds Mol Instincts



Spiramycin C43h74n2o14 Pubchem



Spiramycin A Reappraisal Of Its Antibacterial Activity Abstract Europe Pmc
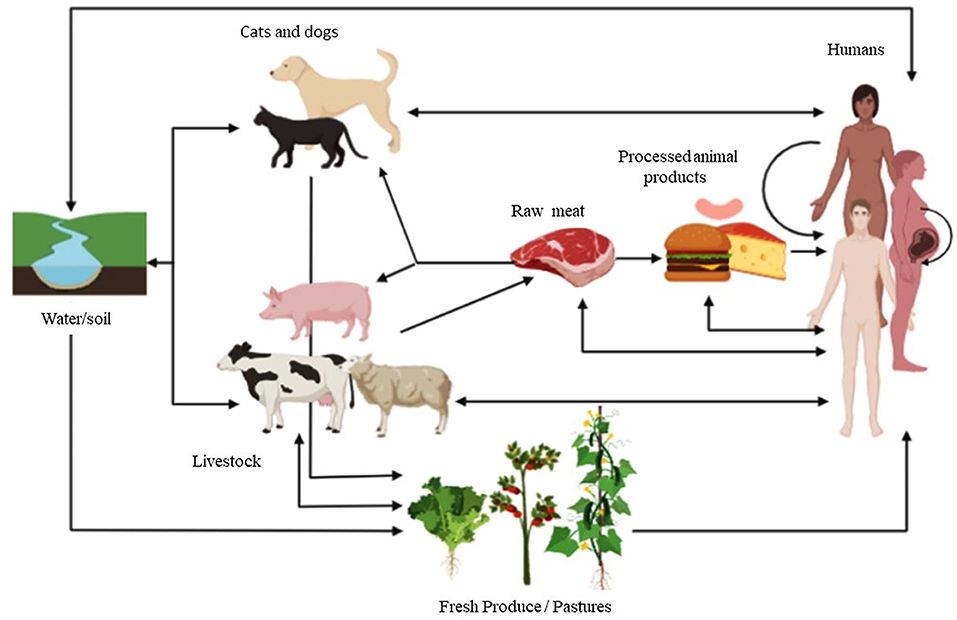



Frontiers Use Of Veterinary Vaccines For Livestock As A Strategy To Control Foodborne Parasitic Diseases Cellular And Infection Microbiology



Spiramycin Drug Monograph Druginfosys Com



Spiramycin Injection



Http Whqlibdoc Who Int Hq 19 Mnh 44 Eng Pdf




Glycosylation Steps During Spiramycin Biosynthesis In Streptomyces Ambofaciens Involvement Of Three Glycosyltransferases And Their Interplay With Two Auxiliary Proteins Antimicrobial Agents And Chemotherapy




Pdf Spiramycin Renaissance
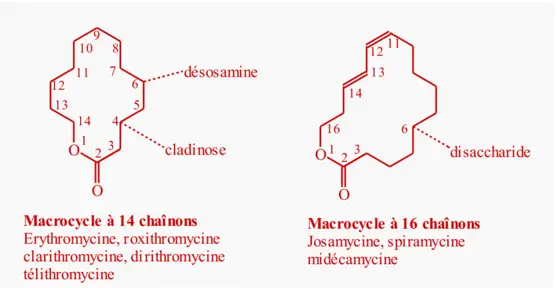



Macrolide Lincosamine Streptogramine



1



Macrolides Et Apparentes C Spiramycine
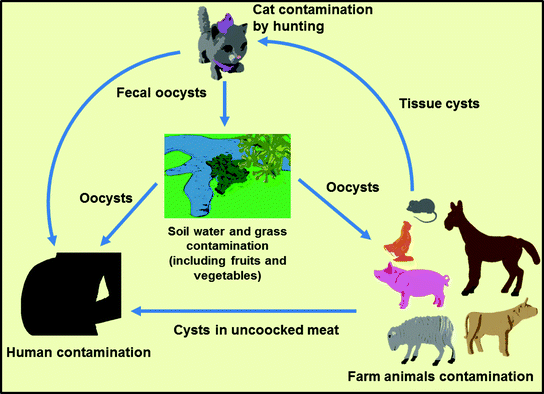



A Comprehensive Review Of Toxoplasma Gondii Biology And Host Cell Interaction Challenges For A Plant Based Vaccine Springerlink



Chemidplus 8025 81 8 Spiramycin Usan Inn Ban Similar Structures Search Synonyms Formulas Resource Links And Other Chemical Information




Spiramycin Wikipedia
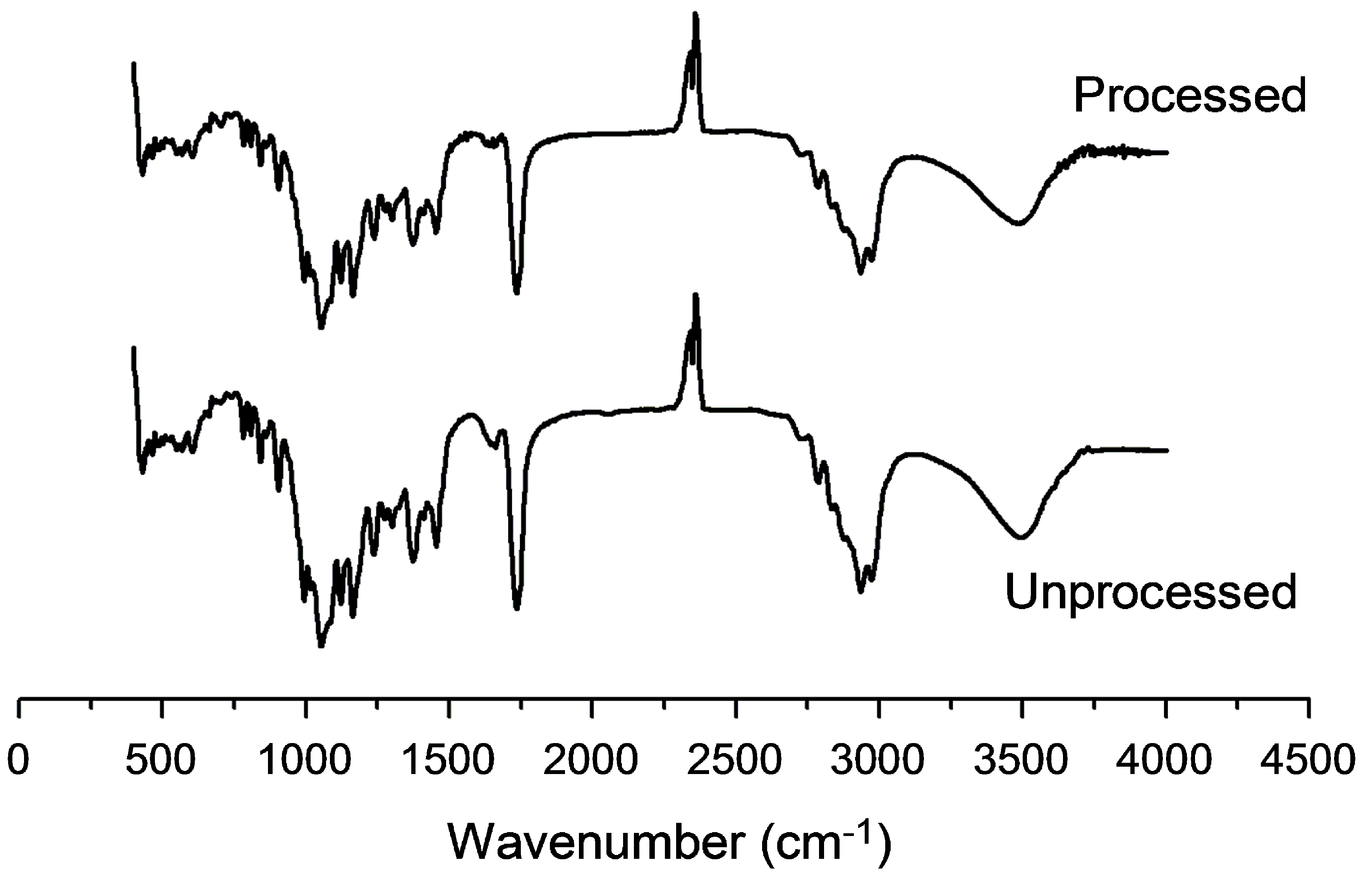



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html



Toxoplasmosis Disease Malacards Research Articles Drugs Genes Clinical Trials



Spiramycin A Reappraisal Of Its Antibacterial Activity Abstract Europe Pmc



Onlinelibrary Wiley Com Doi Pdf 10 1111 J 1600 051x 1994 Tb X



Spiramycin A Reappraisal Of Its Antibacterial Activity Abstract Europe Pmc
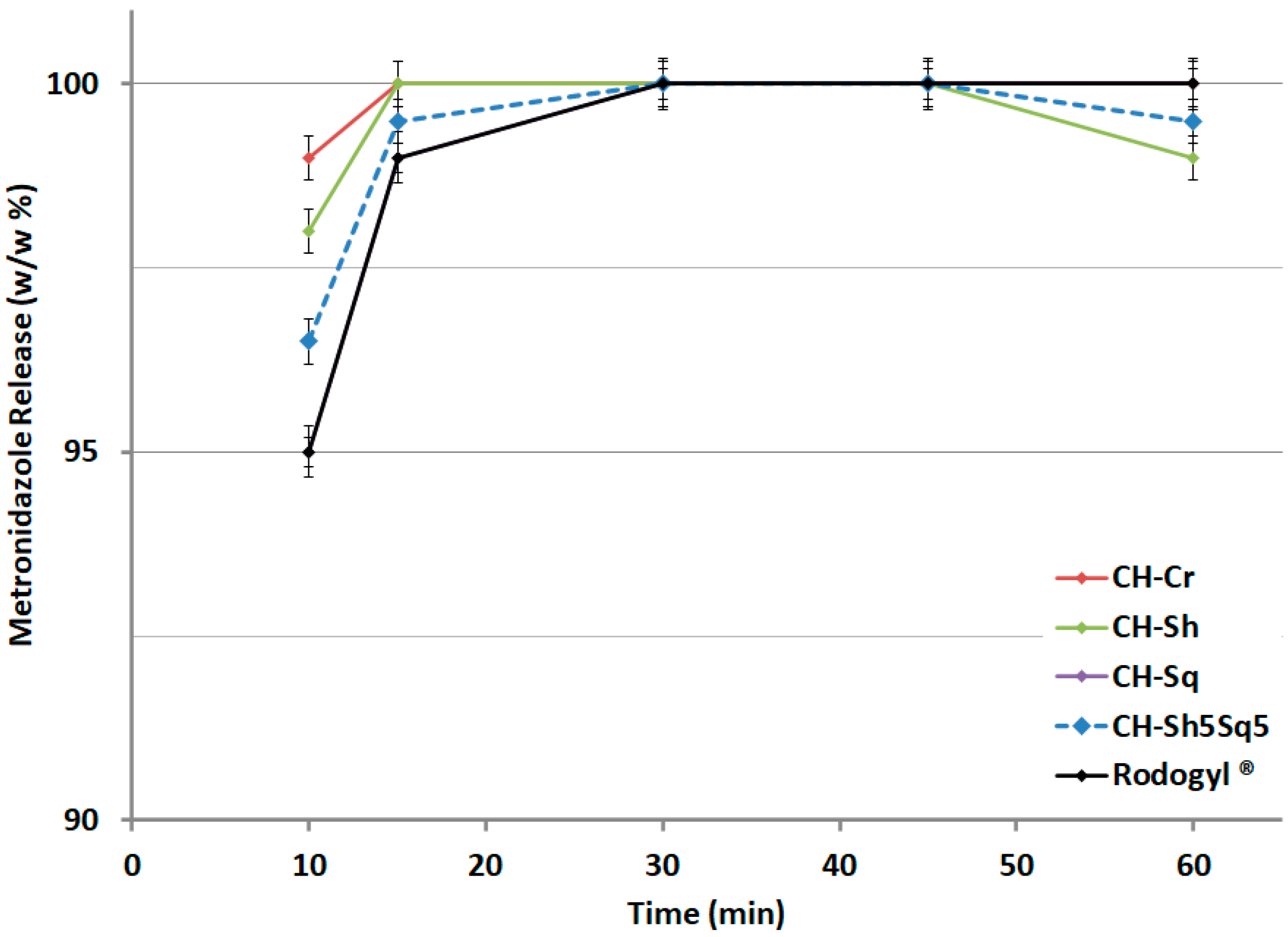



Molecules Free Full Text Influence Of Chitin Source And Polymorphism On Powder Compression And Compaction Application In Drug Delivery Html



Onlinelibrary Wiley Com Doi Pdf 10 1111 J 1600 051x 1994 Tb X




Spiramycin 8025 81 8



Apicomplexa Structure Ppt Video Online Download




Spiramycin I 50 5
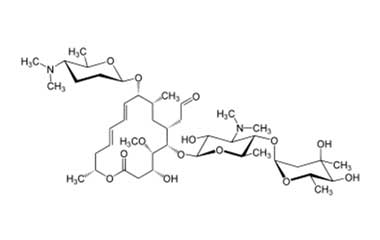



Spiramycin Impurities Pharmaffiliates




Imidazoles Instagram Posts Photos And Videos Picuki Com
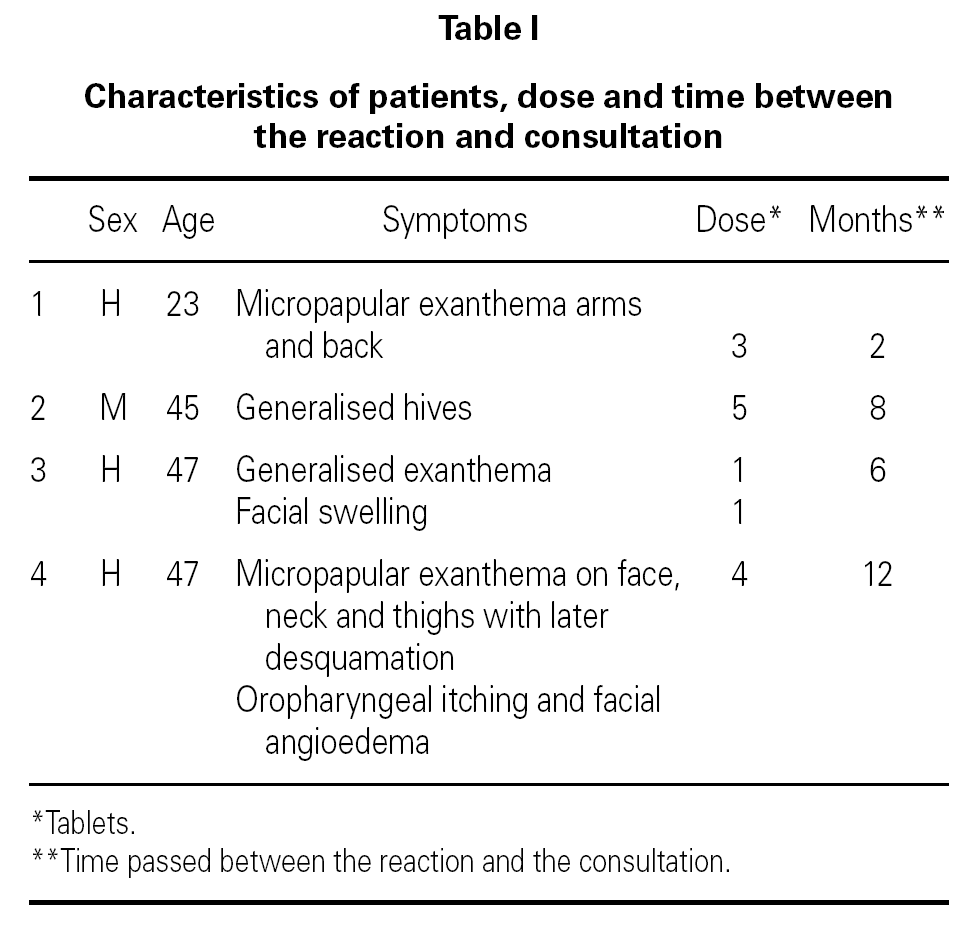



Hypersensitivity Reactions To Metronidazole Allergologia Et Immunopathologia




Drug Induced Acute Interstitial Nephritis Kidney International
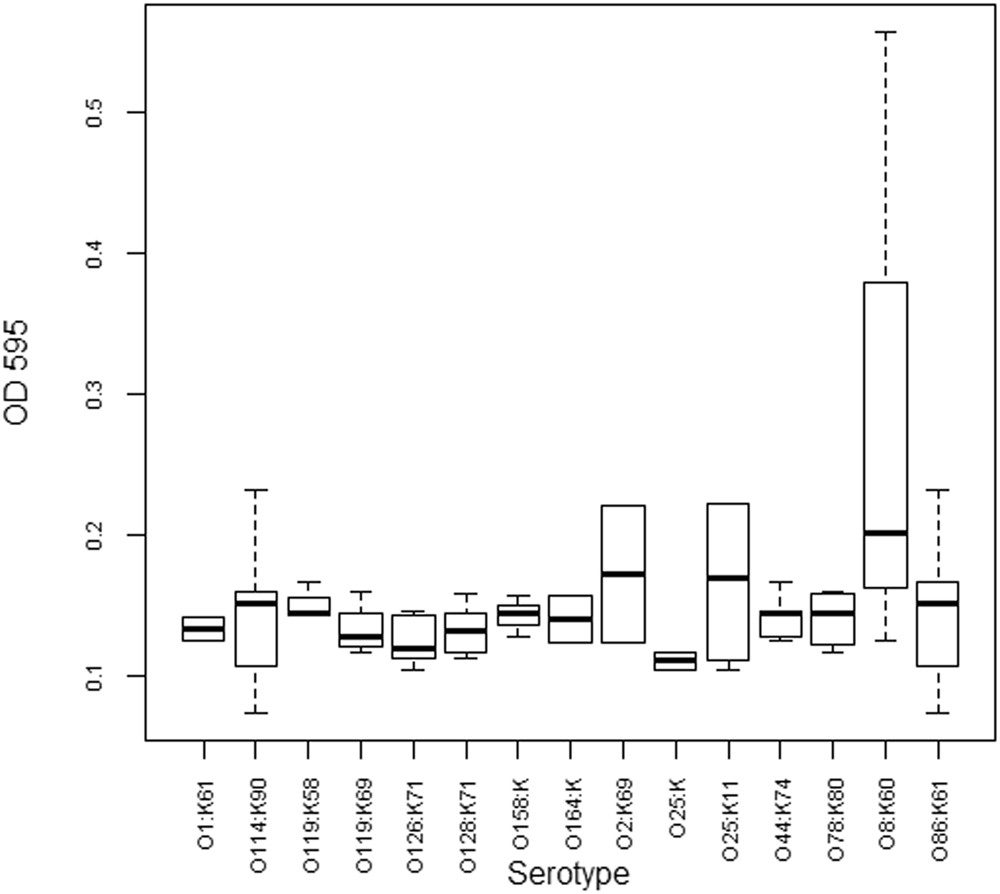



Poultry Hatcheries As Potential Reservoirs For Antimicrobial Resistant Escherichia Coli A Risk To Public Health And Food Safety Scientific Reports




Adsorption Of Metronidazole And Spiramycin By An Algerian Palygorskite Effect Of Modification With Tin Sciencedirect
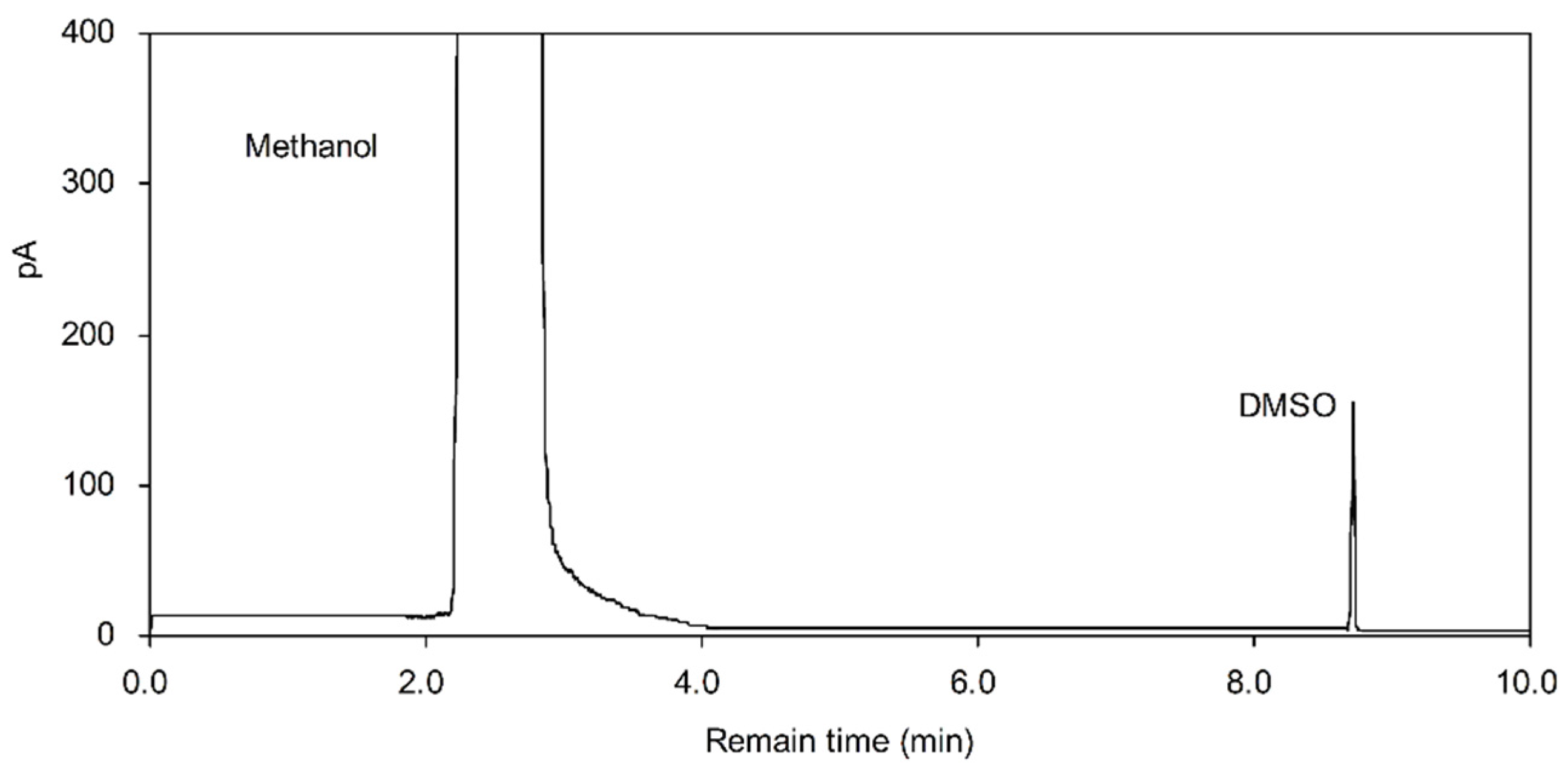



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html




Antibiotics Ppt Video Online Download



1




Oleandomycin Wikipedia



Metronidazole High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



Macrolides Et Apparentes C Spiramycine




Expanding The Therapeutic Spectrum Of Artemisinin Activity Against Infectious Diseases Beyond Malaria And Novel Pharmaceutical Developments Efferth T Romero Mr Bilia Ar Osman Ag Elsohly M Wink M Bauer R Khan I
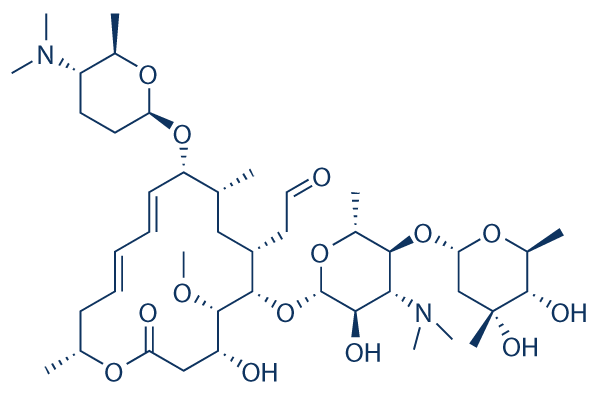



Spiramycin 99 Hplc Selleck Antibiotics Chemical



Spiramycin スピラマイシン New Drug Approvals



Electrospray Mass Spectrum Tic Of Cysteyl Spiramycin I M Is Download Scientific Diagram
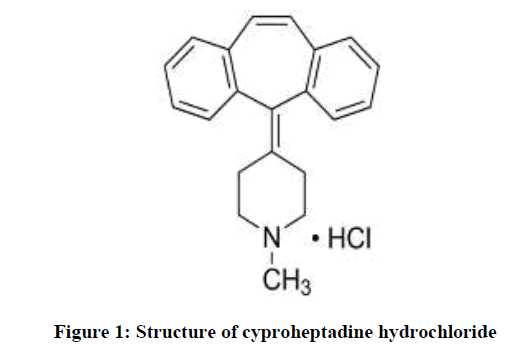



Electrodes Preparation Of Cyproheptadine Hydrochloride Imprinted Polymer Based On Pvc Matrix Membrane
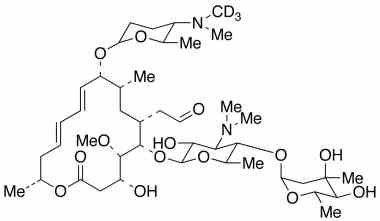



Spiramycin Impurities Pharmaffiliates



Www Ema Europa Eu Documents Mrl Report Spiramycin Summary Report 2 Committee Veterinary Medicinal Products En Pdf



Sansvigyl Cong Ty Cổ Phần Y Dược Phap Au




Definitions Et Medicaments Flashcards Quizlet




Acetyl Spiramycin Spiramycin Adipate Spiramycin Base Manufacturers And Suppliers Price Fengchen




Acetyl Spiramycin Spiramycin Adipate Spiramycin Base Manufacturers And Suppliers Price Fengchen
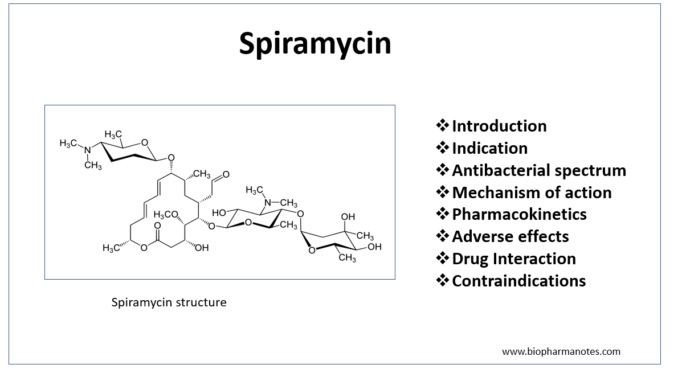



Pharmacology Of Spiromycin Biopharma Notes
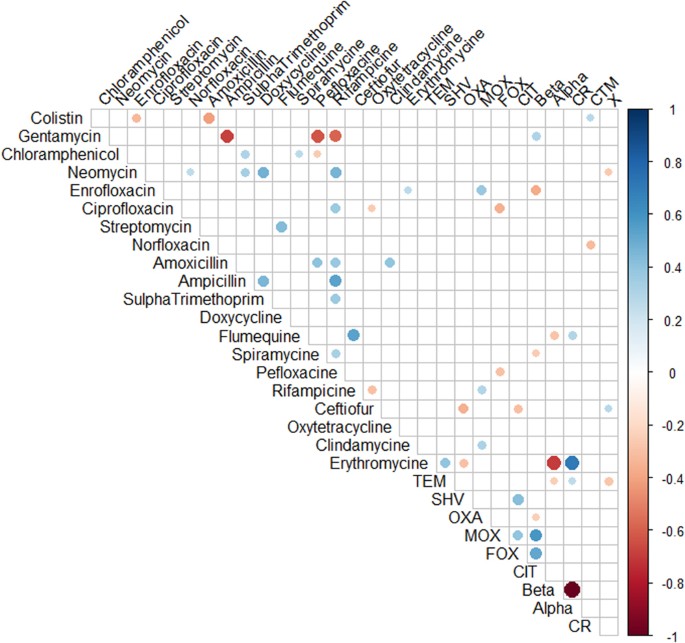



Poultry Hatcheries As Potential Reservoirs For Antimicrobial Resistant Escherichia Coli A Risk To Public Health And Food Safety Scientific Reports
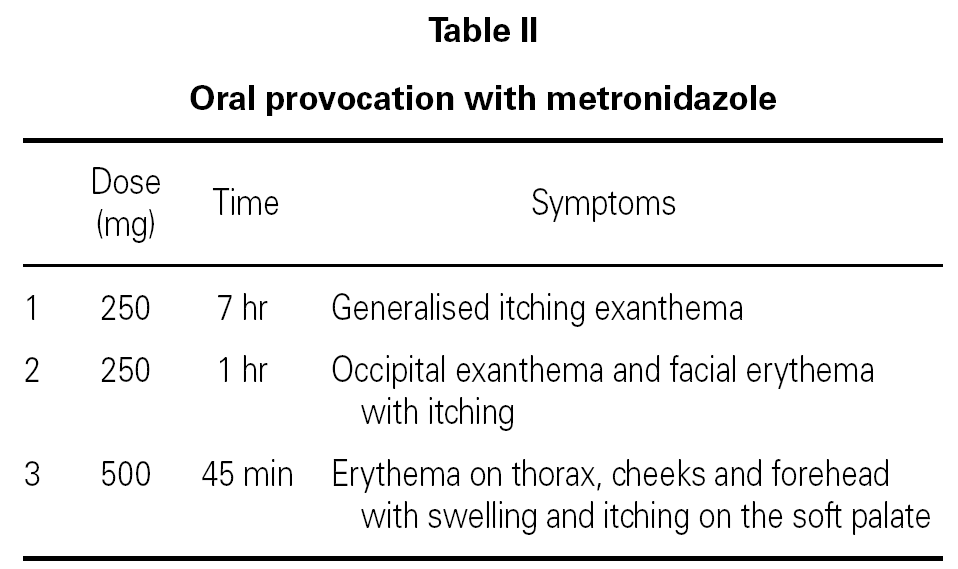



Hypersensitivity Reactions To Metronidazole Allergologia Et Immunopathologia




Identification Of A Bioactive 51 Membered Macrolide Complex By Activation Of A Silent Polyketide Synthase In Streptomyces Ambofaciens Pnas




Apicomplexa Structure Ppt Video Online Download



Tel Archives Ouvertes Fr Tel Document
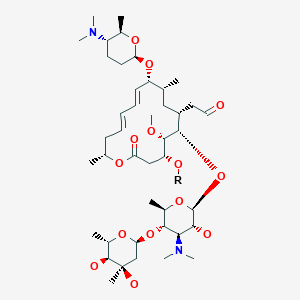



Spiramycin スピラマイシン New Drug Approvals




Adsorption Of Metronidazole And Spiramycin By An Algerian Palygorskite Effect Of Modification With Tin Sciencedirect




Antibacterial Inactivation Of Spiramycin After Titanium Dioxide Photocatalytic Treatment Sciencedirect
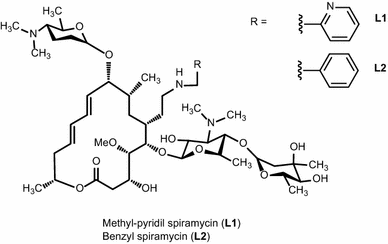



Adenine Nucleotide Recognition By Spiramycin And Some Of Its Aromatic Derivatives Springerlink
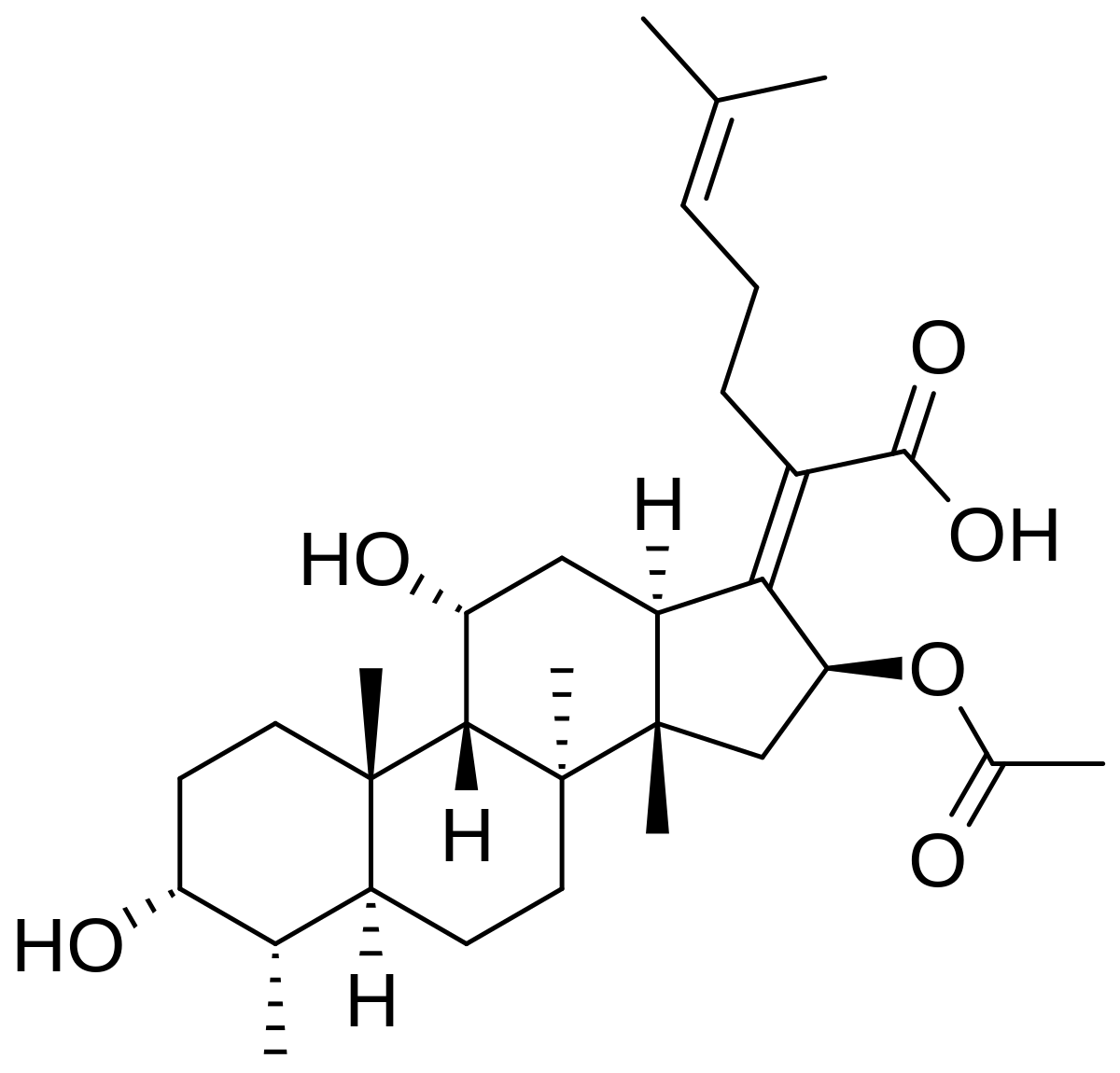



Fusidic Acid Wikipedia
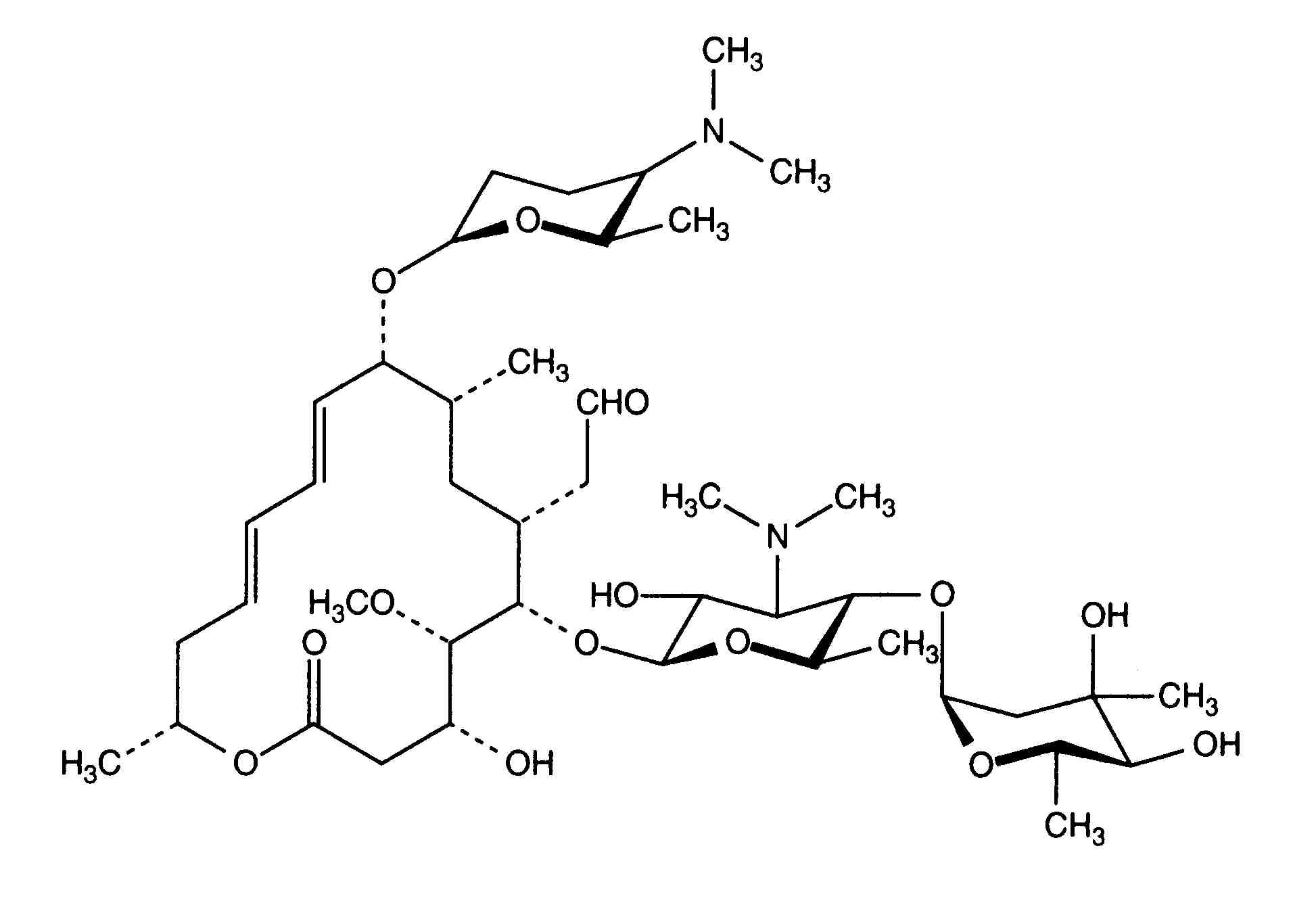



Monographie Spiramycine Adipate Stabilis 4 0




Spiramycin Semantic Scholar




Antibacterial Inactivation Of Spiramycin After Titanium Dioxide Photocatalytic Treatment Sciencedirect




Spiramycin Structure C43h74n2o14 Over 100 Million Chemical Compounds Mol Instincts




Is Chloramphenicol For Dogs Safe Ballya




Chemical Structures Of Main Components Of Spiramycin And Its Related Download Scientific Diagram


